AWS Overview Course
https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/learn/course/9496/play/32556/welcome-to-solutions-architect-associate-exam-prep
- Overview about the certificate
- Domain 1: Resilient architrectures
- Domain 2: High-performing architectures
- Domain 3: Secure Applications
- Domain 4: Cost-optimized architectures
Overview about the certificate
What this certificate covers
This certificate proves that you are able to design and implement systems on AWS, the system you designed have high resiliency, have high performance, have good security, and is cost optimized.
Domain 1: Resilient architrectures
Multi-tier solutions
Exam item will require you to understand and implement several aspects across topics.
Multi-tier solutions refers a general framework that divides up independently scalable applications components, that can be independently developed, managed, and maintained from each other.
Access pattern
Refers to what kind of pattern does the user do to access data? Does it have a peak at certain days, and it everyday.
High availability vs fault tolerance
High availability: Design for a minimum downtime, reducing the negative impact on the end user (the clients who are using the applications), by focusing on restoring the important services when a component or application fails.
Fault tolerance: Design an architecture that have zero downtime and service interruption, but much higher cost of operation due to replication and redundancy.
So basically fault tolerance means that if one part of the architecture failed, there is immediately another part that kicks in to replace that failed part. While, high availability just means you are trying to reduce downtime, minimizing the impact on the user when you are trying to restore the failed application.
Single point of failure
To assess single point of failure, it is helpful to think backwards from the point of failure. Work backward, see what happens if one of the web server failed, the database failed, and so on until you see the single point of failure
Disaster recovery objective
Recovery time object: Measures how quickly after an outage an application must be available again
Recovery point objective: Refers to how much data loss your application can tolerate. How old can the data be when this application is recovered? Is it 5 seconds before the disaster? 3 seconds? The lower the time, the better.
The lower the better for both of these objective

Disaster recovery strategy
Active/passive: Creates an environment that is not intended to be live for IT production until a disaster occurs. This have large initial cost savings on the architecture.
It is further divided into different kind of active/passive strategy:
- Backup & restore: RPO/RTO in hours. Lower priority use cases, supplying the AWS resources after disaster, and restore a backup prior to the event. Cost = $
- Pilot light: RPO/RTO in 10s of minutes. Provision some AWS resources after the event then scale accordingly. Cost = $$
- Warm standby: RPO/RTO in minutes. A scaled down version of the business critical application and is always running can be run into a different region. Then scale up the AWS resources after the event have occurred. Cost = $$$
Active/active: Deployment of a second identical live architecture that continually replicates with the first site. However, it has high cost and the requirement for high bandwidth with low latency.
Both have ideal use cases, and don't have to be used independently
Decoupling mechanisms
Refers to components remaining autonomous and unaware of each other as they complete their work as part of a larger system. Essentially, break down your architecture into components that can function completely independently of each other.
Synchronous decoupling
Involves at least two components, both must always be available in order for things to function properly
Asynchronous decoupling
Decoupling involves communication between components through more durable components.
Ex: Multiple instances that are processing messages, the messages are stored into a queue, and if the instances are down the messages are persisted inside the queue until the instances are restored.
Queues
AWS queue services are usually used as a decoupling mechanism to serve as the durable component for communication between two independent components.
AWS standard queue is best-effort ordering that ensures messages are generally delivered in the same order as they are sent, but occasionally say more than one copy of a message might be delivered out of order.
AWS FIFO queue offer first-in-first-out delivery and exactly once processing. Meaning it is a true queue.
Resilient storage
To understand how to pick a resilient storage you need to go through the following process
- Define the strategy to ensure durability of your data
Know how different storage handle durability and what scenario each storage is suitable for, when to use EC2 store? Amazon S3 glacier?
Knowing this will allow you to pick the correct solution. - Define how data service consistency will affect the operation
Know how the data consistency are done, since it impacts how you retrieve the data and the type of data that you get back.
Also you also need to know the functionality of each storage service. If you have a read-heavy load use this, if you deal with global vs single IP range use that. Knowing access pattern will let you pick the best services - Know how to implement across a variety of architectures, including hybrid or non-cloud native applications
Know that there are other services outside of AWS being incorporated into the architecture.
Domain 2: High-performing architectures
Elastic vs scalable
Although they both mean adapting to dynamic environments they don't really mean the same thing.
Scalable means that you are allocating resource expansion on a more persistent level to meet workload growth. Take the example of pizza place, you notice that there is a steady growth in the popularity of pizza demand, so as the owner of a pizza chain you decided to open up another pizza restaurant anticipating the future growth. It is more permanent.
Elastic means that you are dynamically allocating resources to existing infrastructure in reaction to immediate demand fluctuations, there is a sudden pizza demand because of say Super Bowl or World Cup you would allocate more baker and cashier for your restaurant chain for that day, then the next world it would resume a normal operation.
As you can see scalable is more permanent, and elastic is on the fly for that specific peak demand. They work together to reduce cost while also ensuring that customers are meeting their demands.
Elastic and scalable compute solution
Just because your application is hosted on AWS it doesn't necessarily mean it is inherently scalable by default.
How scalable they are depend on what services you have chosen and how have you configured them.
Some services are scalable by default without you having to do anything, AWS Lambda is scalable and elastic by default, you don't need to make more AWS Lambda instances to scale up, or elastic.
EC2 on the other hand is not inherently scalable, but you can configure it to be scalable. You need to know what your application needs are, before you can choose the instance type. You should be able to pick the appropriate EC2 instance type for the corresponding workload.
Cloudwatch alarm
This is used to trigger scaling event, and you would have to pick a metric to monitor and use as a deciding factor on when to scale up your application.
The common metric that is used for monitoring is CPU utilization.
High-performing and scalable storage solution
Each storage solution have its use cases, and scaling ability. EBS vs S3 or EFS.
A EC2 attached to a EBS volume, when that EBS volume fills up it will not automatically increase the volume on its own.
A EC2 attached to a EFS filesystem, the filesystem will grow and shrink automatically without you have to do anything as you remove or add files.
You should also determine which storage solution is the best fit based on future storage needs. Each storage service also have a upper bound limit, the maximum size capacity.
Performance
You should also be able to determine which storage you should use according to its performance, the IO access speed is it fast or is it slow?
EBS volume are extreme low latency, but they can be configured to have a certain latency depending on the use cases.
Performance improvement
You should be familiar with some of the API that you can use to increase performance of data uploads or data retrieval.
For S3, data upload know the API or CLI command. Multipart uploads. Amazon S3 accelerator. Caching with Amazon CloudFront to improve retrieval speed.
High-performing networking solutions
You should be able to pick the best networking solutions for a workload given a set of requirements or circumstances.
Under a hybrid system, a company might still be hosting some data center for part of their application, and the other part utilizing AWS. The data center and the AWS architecture need a secure way of transfering data and messages across these two different system, securely and reliable.
You can connect data center and AWS via AWS managed VPN or AWS Direct Connect. Which one to pick will depend on the use cases, and their performance differs.
AWS Transit gateway, can be used with VPN or direct connect, to connect multiple VPC to a remote network.
Direct connect
High-speed, low-latency connection that let you connect on-premises (local) infrastructures to AWS services. The connection is made possible by dedicated lines and bypasses public internet to reduce network unpredictability and congestion.
However, the ease of use is not there.
AWS VPN/Site-to-Site VPN
Let you create an encrypted connection between Amazon VPC and your on-premise infrastructure over public internet.
It let you connect existing on-premise network to your AWS VPC as if they were running locally.
It is easy to set up and install.
AWS transit gateway
You would use transit gateway to connect multiple VPC together with on-premise network.
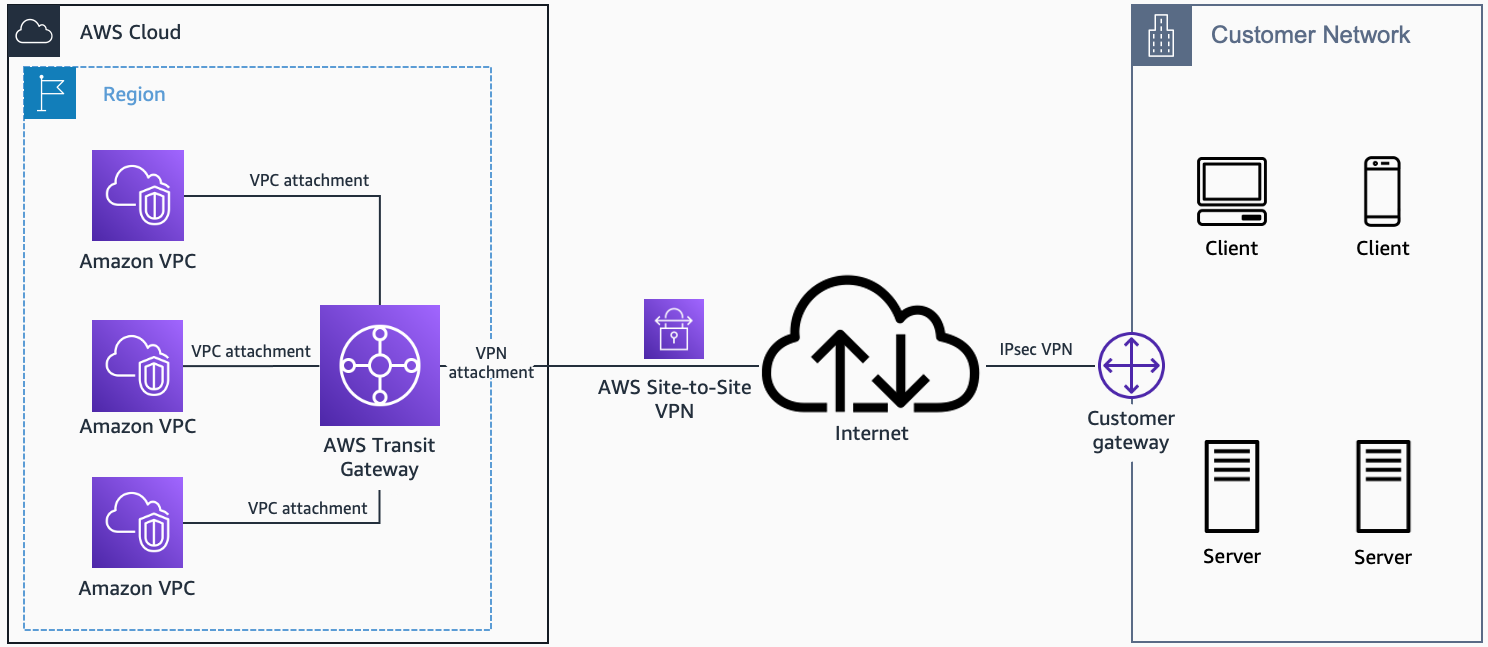
AWS VPN CloudHub
If you have multiple on-premise sites then you can use VPN Cloudhub to connect the VPC to all of those on-premise sites in a secure manner

Connectivity between VPCs
- VPC peering: Point to point network connectivity between two VPCs only. But you can create a full mesh network that uses individual connections between all networks. This will require lots of work if you are planning to connect multiple VPCs with each other.
- AWS Transit gateway: You can use this to solve the problem with VPC peering, creating a full mesh network all interconnected connections are much easier with transit gateway. You can connect existing VPCs together.
- AWS PrivateLink: Doesn't use public internet for access services hosted on AWS. It connects services and not VPCs together.
- AWS Managed VPN: Used for establishing connection between on-premise and VPCs
Amazon Route 53
Route 53 has a feature called geopromixity routing that routes the user request to the AWS service that is physically closest to the user.
Route 53 is a DNS server.
AWS Global Accelerator
Improves availability and performance for your public internet applications
Also consider caching using AWS CloudFront to improve performance.
Data transfer services
Multiple ways of transferring data to AWS that you should be familiar with.
- AWS DataSync
- AWS Snow Family
- AWS Transfer Family
- AWS Database Migration Service
Depends on the amount of data, type of data, destination, and source one will be better than the other.
High-performing database solutions
Need to know which services need to use non-relational, relational, and graph databases.
Amazon RDS can be high performance, but DynamoDB
Know the performance differences database services, RDS vs Aurora.
Aurora is MySQL and PostgresSQL compatible relational database. Have performance, availability, simplicity, and is cost effective. Compared to RDS, the performance is higher and more consistent.
RDS is managed SQl database, easy for provisioning, setup, patching, and backup.
RDS Storage types
General purpose SSD: This is for general cost-effective general use. Best for development and testing environments.
Provisioned IOPS SSD: Designed to meet intensive I/O intensive workloads. Best for production environments.
Magnetic: Used for backward compatibility. For workloads where data is accessed less frequently and small database.
Scaling strategies
Amazon DynamoDB scales storage under the hood automatically, but you also still have control over scaling throughput or you can auto scale as well to increase or decrease scaling on the throughput.
RDS also let you do auto scaling for storage, but to scale CPU usage you need to update the DB instances.
Database caching
Different database have caching features that you should be familiar
Domain 3: Secure Applications
Secure resource access
Security should be considered at every level, stage, and architecture.
The biggest security decision you make early is how the people tool and applications you build will access the necessary AWS resources. It will tell you how to manage the access that is given.
Identity and access management is how you will be giving access. How you create them, what kind of strength they have. Users and groups.
Least privilege.
Never hard code credentials into your application!
Learn about policy statement.
How does the IAM use policy statement.
Secure application tiers
Network ACLs and security groups provide security for the network traffics. It lets you control the incoming and outgoing traffics. You will have to add rules to control the traffic based on the protocol and port numbers.
For example: You can specify for TCP over port 443 to allow it or disallow it for say a EC2 instances.
You can use security groups along with VPC to control traffic that is allowed to leave the resource in a VPC. By default VPC have a default security group that allows all incoming and outgoing traffic for the resources in the VPC if you don't specify one.
External threat
What services can be used to protect against external attack against your applications?
What controls do they provide.
Data security options
How are the data protected during transit or when it is at rest?
How does the data storage services handle data protection? Are they encrypted?
Encryption options
How does the storage services handle encryption? How will the key be handled?
Does encryption affect performance?
AWS Key management service will help you generate, store, and control cryptographic keys.
Domain 4: Cost-optimized architectures
Cost-effective storage solutions
Yous should know which storage service should be used, an object storage, or a file storage and identify the cost optimized storage.
Right-size EBS volumes
Pick the right size, don't over provision more than you need
You need to have a good idea about how much storage you actually need to determine this. AWS Trusted Advisor can help you advise on what kind of volume to pick.
Delete old EBS snapshots that are basically incremental backups if you don't need them.
S3
Object are stored with standard storage class by default in S3, it has high cost for storing the object, but low cost for retrieval of the object.
You can pick different storage class depending on the use case.
- S3 Standard: Highest cost of storing, but very low retrieval cost
- S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent access): Kind of high cost of storing, and a little bit more costly for retrieval
- S3 Glacier: Low cost of storing, high retrieval cost
- S3 Glacier Deep archive. Very low cost of storing, very high retrieval cost
S3 intelligent-tiering can be used for variable or unknown access pattern; to automatically select a tier for your S3 storage.
Cost-effective compute and database services
EC2 pricing models
- On-demand instances: You pay by hour of usage for AWS instances
- Reserved instances: A user locks in a AWS instances for a span of 1 or 3 years and gets a significant discount compared to on-demand pricing. However, the drawback is that reserved instances are assigned to a specific availability zones.
This is different than saving plans because the configuration of the instances is locked, while savings plan you can change the instance configurations as long as you keep using it. - Dedicated instances: No noisey neighbor per say because non-dedicated instances can be run on the same hardware so you will be sharing the hardware with other people. If their usage spike up it might affect your performances. To avoid this you reserve yourself own dedicated hardware without sharing with other people.
- Spot instances: User bid for the price of a spare EC2 instances. A market price is set for a spare instances.
- Saving plans: Apply to EC2 and other services by making a commitment to a consistent usage, for 1 or 3 years.
EC2 size and family
Pick a EC2 instance that is right for your workload. Low utilization you have option to make instane smaller.
Right-sizing EC2 instances and RDS DB instances are a good way to optimize for cost.
Pick the right amount of CPU and RAM to do the job.
However, scaling up is usually costly, so it is best to look for alternatives rather than scaling up all the time.
Database services
Depending on the use case, you should pick the best database.
Use managed services when possible. Remove operational burden of maintaining servers for tasks, like running apps or managaing databases. So basically you removed some of the manual tasks that is required for say maintaining a server, or keep an app up and running in EC2 instances and offload them to AWS.
AWS Lambda you don't have to worry about setting up the servers and everything, just write the code and deploy it ez. Free up the people that are required to manage these things to do something else instead.
Ex: fargate for containers, aws lambda for serverless compute, dyanmoDB for database
Cost-optimized network architectures
Data transfer and API calls might incur costs as well. S3, you pay for the data that you stored, but you also spend money on the API calls that you made to S3.
So the good way to optimize cost is to reduce the amount of API calls and data transfer that is occurring. One solution to this is to use CDN (Amazon CloudFront) as a cache. If the object is found in CloudFront, then it will just be returned, if it isn't then it will request S3 for the object, and send it back.
Connectivity on-premise and AWS
Use AWS managed VPN for data transfer instead of AWS direct connect for more cost-effective solutions.
There are also connect to NAT gateways and transit gateways! Not everything is free bruh.