Software Development Life Cycles
SDLC
Software Development Life Cycles is a step by step structured process that is used to help guide teams on design, develop, test, and deploying your application software.
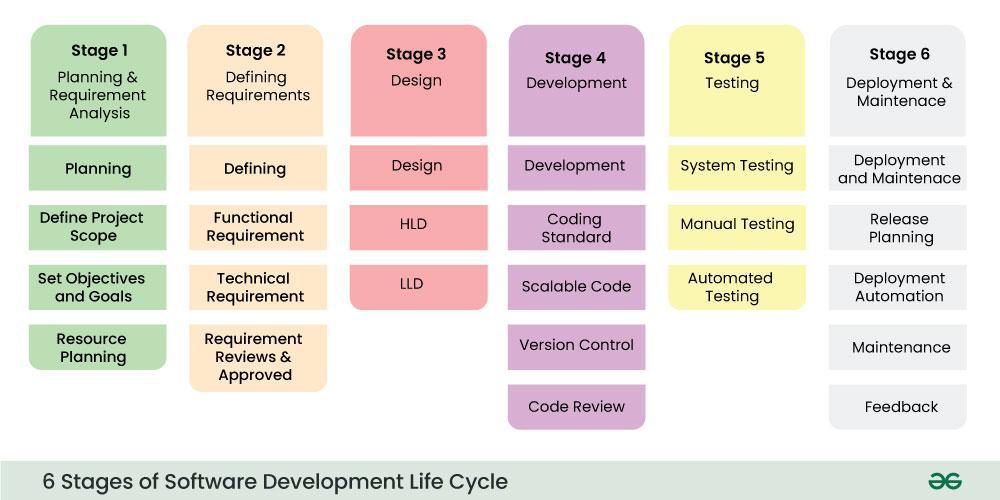
It lay out different phases to follow during a software development cycle:
Planning and Requirements
Analyze what is the need and defining the requirements for building out the project.
Design
Design the architecture.
Develop
This is where you will then do coding
Testing and Integration
Testing the application that you have produced and making sure that it integrates well in the bigger system.
This is where you will be writing unit test, integration test, and conduct even performance test to ensure that your application is able to withstand the expected amount of traffic.
Deployment
Finally, once the product is deemed acceptable in a lower environment this is when you will be doing deployment into production to take in the live traffic.
SDLC Model
Given that the SDLC is just a guideline there are different methods of implementing it.
- Agile: This is what is been more popular now with software engineers. Agile thrives on continuous feedback and adaptations. You deliver software in small but iterative cycles that's referred to as sprints. The requirements are continuously evaluated, planned so that changes can be responded quickly.
- However, this can subject your team to a lot of scope creep
- Waterfall: This is the most traditional model for executing Software Development Life Cycle. You will plan out each of the phases, and then execute each of the phases in sequential. You will only move on to the next phase once the prior phase has been completed.
- This model have pros in the sense that each phases have clear goal and is well defined making it easy to follow and use. There are minimal scope creep since you defined everything from the planning phase.
- However, there are cons as well, there are inflexibility with using the waterfall model. Once you committed to a project it will be hard to change / revise the requirements. It is also resource intensive if there are changers needed after the project has began.
No comments to display
No comments to display